IBM 量子開発者認定資格 v2.X sample問題集の解説 その2
新しいQiskitのバージョンに対応した資格である、「IBM Certified Quantum Computation using Qiskit v2.X Developer - Associate」がリリースされました。
この資格を取得することでqiskitや量子プログラミングに関する知識を証明することが可能です。
この認定を得るためには、上記リンクに記載がある通り、“Exam C1000-179: Fundamentals of Quantum Computing Using Qiskit v2.X Developer”という試験に合格する必要があります。 IBMはこの試験に関するsample問題集も公開しており、上記URLリンク内の「Sample Test」で公開されています。 ただ、こちらのSample問題集では解説は特に記載されていないため、なるべく分かりやすく解説を記載します。このページでは11 ~ 21問までの解説を記載しています。1 ~ 10問の解説についてはこちらのページをご参照ください。
IBM量子技術者試験問題集
最新の試験バージョンである”IBM Certified Quantum Computation using Qiskit v2.X Developer - Associate”に対応した問題集がリリースされました。この問題集で、スコアを伸ばし、合格率を上げましょう。
はじめての量子コンピューター入門【基礎知識・Qiskitでの実装・量子機械学習 全て学べる】
量子コンピューターの入門コースを作成しました。このコースにより、量子コンピューターの基礎知識、Qiskitでの実装、量子機械学習について学べます。
Amazon Braket学習コース
また、AWSでの量子コンピューティングサービスであるAmazon braketについての学習コースもリリースされています。 量子コンピュータやAWSの知識が無い方でも学び始められ、最終的には量子機械学習についても学べます。
問題11:
Which code fragment is the correct way to open a session?
選択肢:
- A.
from qiskit_ibm_runtime import Session
session = Session(system='ibm_foo')
- B.
from qiskit_ibm_runtime import execute, QiskitRuntimeService
service = QiskitRuntimeService()
session = execute(service=service)
- C.
from qiskit_ibm_runtime import Session, QiskitRuntimeService
service = QiskitRuntimeService()
session = Session(service.least_busy())
- D.
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit
session = QuantumCircuit(2).open_session()
回答: C
解説: sessionを正しく開くコードはどれですか?という問題ですね。こちらのページの問題10での説明の通り、sessionはVQCなどの量子―古典アルゴリズムを実行する際に便利な機能です。また、sessionの利用方法はこちらに記載があります。このサイトからも確認できるように、Cが正解のコードとなります。A、B、Dについては実行するとエラーになります。
問題12:
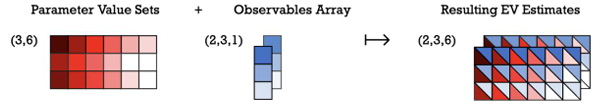
Which one of the following patterns, expressed in terms of array broadcasting primitives, is represented by the given image?
選択肢:
-
A. Standard multidimensional array generalization
-
B. All-to-all
-
C. Extended dimensional variation
-
D. Best effort broadcasting
回答: A
解説: 配列のブロードキャストの基本操作で表されるパターンとして、与えられた画像が示しているものはどれか?という問題ですね。VQCなどの量子機械学習アルゴリズムなどでは、図で記載されているように、複数のParameter Sets、複数のObservables(演算子)について、期待値を求めたい場合があります。 Parameter Sets、Observablesが共に複数のケースで計算を行った際、期待値はどのような形式で得られるかについて、「Primitive inputs and outputs」で紹介されています。このページにも記載がある通り、この計算はStandard multidimensional array generalizationに該当しているため、Aが正解です。
問題13:
Given the following code fragment, which one of the following describes the SamplerOptions parameter options.default_shots?
...
from qiskit_ibm_runtime import Sampler
sampler = Sampler(mode=backend)
sampler.options.default_shots = ...
選択肢:
-
A. The sum of the number of measurements in each qubit
-
B. The number of randomizations we apply to the circuit
-
C. The number of times that we run the circuit
-
D. The number of sequences in dynamical decoupling
回答: C
解説:
SamplerOptions パラメータoptions.default_shotsが表すものは次のうちどれですか?という問題ですね。量子コンピューターはエラーが発生しやすいため、量子回路を複数回実行、測定します。Samplerでのshotsは、回路を何回繰り返して測定するかを示し、Cが正解となります。ちなみに表示されているコードについて、例えば以下の様に設定し、samplerを実行すると、デフォルトで300回の実行が設定されます。
sampler.options.default_shots = 300
問題14:
Given the code snippet, which one of the following is a valid way to invoke the run method on an instance of SamplerV2?
from qiskit_ibm_runtime import SamplerV2
...
sampler = SamplerV2(...)
選択肢:
-
A.
sampler.run([isa_circuit]) -
B.
sampler.run(distribution, isa_circuit) -
C.
sampler.run(isa_circuit, distribution='gauss') -
D.
sampler.run([isa_circuit1, isa_circuit2], runs=1024)
回答: A
解説:
SamplerV2クラスのrun()メソッドを正しく呼び出しているコードはどれか?という問題ですね。run()メソッドについてはこちらに利用方法が記載されており、この問題ではAで正しく回路を実行可能です。B、Cについて、distribution という名前の引数はrun()に存在しないため誤りです。Dについてはrunsをshotsに変更すれば実行可能です。ちなみにこの場合は、isa_circuit1, isa_circuit2がそれぞれ実行され結果が格納されます。
問題15:
Which one of the following describes the expected behavior of the number of shots if the value for the parameter precision were changed from 0.015625 to 0.03125?
選択肢:
-
A. It increases the number of shots quadratically
-
B. It increases the number of shots exponentially
-
C. It has no effect on the number of shots
-
D. It decreases the number of shots
回答: D
解説: パラメータprecisionの値を0.015625から0.03125に変更した場合、ショット数についてはどうなるか?という問題ですね。default_precisionと、default_shotsについてはこちらで少し解説があります。backend_estimator_v2のソースコードからも確認できますが、precisionを大きくすると(精度を荒くすると)、shotsの数は少なくなります。このため、Dが正解となります。
問題16:
Which error mitigation technique can be applied using resilience options?
選択肢:
-
A. Pauli twirling
-
B. Dynamical decoupling
-
C. Zero Noise Extrapolation
-
D. Full quantum error correction
回答: C
解説: 「resilience options」を使って適用できるエラー軽減手法は次のうちどれか?という問題ですね。 resilience optionsは、ノイズに強い計算結果を得るためのオプションです。詳細についてはこちらで記載されており、「Zero-Noise Extrapolation error mitigation method」が利用可能です。これは、ノイズをあえて増やした結果も確認することで、ノイズ0の計算結果を推測する手法です。このため、正解はCとなります。A、B、Dはresilience optionsでは利用できません。
問題17:
Which format should a primitive unified bloc (PUB) tuple follow for the Estimator primitive?
選択肢:
-
A.
pub = (circuit, observable, parameter_values, backend) -
B.
pub = (circuit, observable, parameter_values, precision) -
C.
pub = (circuit, observable, shots, optimization_level) -
D.
pub = (circuit, observable, resilience_level, noise_model)
回答: B
解説:
Estimator primitiveにおいて、PUBタプルはどの形式に従うべきか?という問題ですね。
Estimator primitiveでは与えられた量子回路(circuit)、演算子(observable)、パラメーター(parameter_values)について、期待値を算出可能です。さらにEstimator primitiveでは、問題15で登場したprecisionも指定可能なのでBが正解となります。
ちなみにEstimator primitiveを使ってVQCなどの量子機械学習を実行する場合は、circuitには対応するデータの情報と機械学習モデルが組み込まれ、parameter_valuesには機械学習モデルのパラメーターが設定され、observableには出来上がった機械学習用の量子回路から結果を得るための演算子が定義されます。量子機械学習について学ばれる場合はこちらのコースもご活用ください。
問題18:
Which statement describes the purpose of a Qiskit Runtime session?
選択肢:
-
A. Automatically generate quantum algorithms based on user input
-
B. Visualise the results of quantum experiments in real time
-
C. Group a collection of calls to the quantum computer
-
D. Compile and optimise quantum circuits for different backends
回答: C
解説:
Qiskit Runtime sessionについて、正しく説明しているのはどれか?という問題ですね。
こちらで解説している問題10でも記載した通り、sessionモードでは、システムを独占的に使用できる専用の時間枠が設けられます。
VQCや、VQEなどの変分アルゴリズムでは、古典コンピューターでの計算と量子コンピューターでの計算が交互に行われますが、計算のたびに他のユーザーのジョブを待機していると非常に時間がかかってしまいます。このモードを用いることで、量子コンピューターの呼び出しをまとめられ、変分アルゴリズムを高速で実行できるようになります。このため正解はCとなります。
問題19:
Which two of the following pieces of information are part of the dictionary returned by session.details(), assuming that session is an instance of qiskit_ibm_runtime.Session?
選択肢:
-
A. Quantum circuit depth
-
B. Timestamp of the last job in the session that completed
-
C. Session state
-
D. Primitive options
-
E. Primitive unified blocs (PUBs) in each job
回答: B, C
解説:
sessionがqiskit_ibm_runtime.Sessionのインスタンスである場合、session.details()が返すdictionaryに含まれる情報で正しい2つはどれですか?という問題ですね。
session.details()についてはこちらに情報が記載されています。このページに記載の通り、正解はB、Cとなります。その他の情報についてはsession.details()では取得できません。
問題20:
Which one of the following is a classical data type supported by OpenQASM 3?
選択肢:
-
A. complex
-
B. class
-
C. char
-
D. enum
回答: A
解説:
次のうち、OpenQASM 3がサポートするclassical data typeはどれですか?という問題ですね。
OpenQASM (Open Quantum Assembly Language) 3は、IBMが中心となって開発している量子プログラミング言語です。Classical scalar typesについてはこちらでサポートされる型が記載されており、Aが正解となります。B、C、Dの型はサポートされません。
問題21:
Which method should be used to export a Qiskit circuit named qc to OpenQASM 3 and store it into a file stream named qasmprogram?
選択肢:
-
A.
qc.to_openqasm3(qasmprogram) -
B.
qiskit.qasm3.dump(qc, qasmprogram) -
C.
qasmprogram.export_to_qasm3(qc) -
D.
qiskit.qasm3.export(qc, qasmprogram)
回答: B
解説:
Qiskitの回路qcをOpenQASM 3形式でqasmprogramに保存するには、どのメソッドを使用すべきですか?という問題ですね。
BによりOpenQASM 3形式で保存が可能なため、Bが正解となります。こちらのサンプルコードは例えば以下の通りです。
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit
from qiskit import qasm3
qc = QuantumCircuit(2)
qc.h(0)
qc.cx(0, 1)
with open("bell.qasm", "w") as qasmprogram:
qasm3.dump(qc, qasmprogram)
こちらを実行すると、以下のようなbell.qasmファイルが実行ファイルと同じ置き場に作成されます。
OPENQASM 3.0;
include "stdgates.inc";
qubit[2] q;
h q[0];
cx q[0], q[1];
他のA、C、Dは実行するとエラーとなります。
1 ~ 10問の解説についてはこちらのページをご参照ください。
IBM量子技術者試験問題集
最新の試験バージョンである”IBM Certified Quantum Computation using Qiskit v2.X Developer - Associate”に対応した問題集がリリースされました。この問題集で、スコアを伸ばし、合格率を上げましょう。
はじめての量子コンピューター入門【基礎知識・Qiskitでの実装・量子機械学習 全て学べる】
量子コンピューターの入門コースを作成しました。このコースにより、量子コンピューターの基礎知識、Qiskitでの実装、量子機械学習について学べます。